Digital Storage: How Big Are Gigabytes, Terabytes, and Petabytes?
Have you come across data storage units like Petabytes, Gigabytes, and Terabytes? What do they mean in the real world of data storage? The articles will make you comprehend the complexity of units of data storage and their actual sizes. Let us see how much data capacity you need for your daily storage purposes.
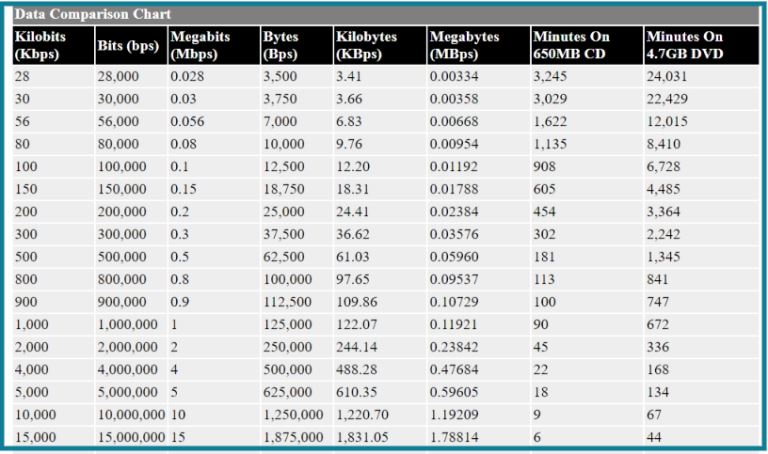
In total, there are 8 units of data volume called bytes. The size of Gigabytes, Petabytes and Terabytes can be calculated by how many bytes compose each. Here is the table to give the exact size of Digital Storage units:
| Unit | Shortened | Capacity | Real-world Example |
| Gigabyte | GB | 1024 Megabytes | 7 minutes of HD TV video |
| Terabytes | TB | 1024 Gigabytes | 1,430 CDs or 213 DVDs |
| Petabytes | PB | 1024 Terabytes | 24/7 video recording at 1080p for almost 3.5 years. |
Note:
- Giga- means 1,000,000,000
- Tera- means 1,000,000,000,000
- Peta- means 1,000,000,000,000,000
Therefore;
- A Gigabyte is a billion bytes.
- A Terabyte is a trillion bytes.
- A Petabyte is quadtrillion bytes.
Units of Data Storage start from the tiniest bit to the largest yottabytes. In this article, you will get complexity explained with real examples, which will make you understand the amount of data capacity you need. So, read on.
Digital Storage: How Big Are Gigabytes, Terabytes, and Petabytes?
It's is so easy to get lost in the data storage terminology universe, especially when talking about digital storage units of measurement. For example, what is the difference between bytes and bits? Terabytes and megabytes? Kilobytes and Yottabytes? Petabytes and Exabytes? It isn't very clear but allows me to make it easier for you.
Probably you have heard about the data storage units terminologies. But what do they mean, and how can we use them in the real world?
The units mentioned above of digital storage are all amounts of digital storage. At times, megabytes and gigabytes can be confused with megabits and gigabits, and so on.
It is essential to know how these units relate to one another and what they mean, especially when comparing data volume sizes on tablets, flash drives, and hard drives. It is also useful when comparing data transfer rates when buying or subscribing to internet services or networking gear.
Before you get to the Gigabytes (GB), there are other smaller units- Kilobytes (KB) and Megabytes (MB), which will be highlighted later in this article.
Let us go deeper into understanding Gigabytes, Terabytes, and Petabytes.
How big is a Gigabyte?
Gigabyte is the most common storage unit in modern devices, and you might be aware of it. However, you might be wondering how big a gigabyte is.
How many bytes are in Gigabyte? Remember that each of the units increases by a multiple of 1,024. There are 1,024 bytes in a kilobyte and 1024 kilobytes in a megabyte. There are 1024 MB in a GB and 1 billion bytes in a GB.
Gadgets known to use Gigabytes as their storage units are smartphones, tablets, USB drives, and
web hosting ( We shall see this kind of storage later).
Real-world examples of a Gigabyte (GB)
- 1 GB holds about 230 standard MP3 music files.
- 1 GB is about 3 minutes 4K videos at 30FPS, depending on the video codes used.
- 1 GB is about 1o yards of books on your shelf.
- 4.7 GB is the capacity for one DVD.
- Streaming Netflix Ultra HD for one hour is about 7 GB.
In today's technology, most phones come with 32GB to 512 GB of storage capacity. However, in computers and hard drives, there are larger sizes. And that is what takes us to the next unit of storage- Terabyte.
How big is a Terabyte?
One terabyte, abbreviated as TB, is made up of 1024 GB. TB is commonly used when measuring the sides of modern hard drives capacity.
Real-world examples of a terabyte (TB)
- One terabyte is equal to 500 hours of movies, 200000 five-minute songs or 310,000 pictures
- 10 TB can store the data produced by Hubble Space Telescope per year
- 24 TB equals the data uploaded on YouTube per day back in 2017.
How big is a Petabyte?
One petabyte (PB)- made up of 1024 or around one million GB. There is a high possibility that petabytes will replace TB soon, as consumers use the standard measurement of shared hard drives and other gadgets.
Real-Word Examples of a Petabyte (PB)
- 1 PB can store 745 million floppy discs or 500 billion standard types of text pages
- 1.5 PB can store 10 billion Facebook pictures
- The amount of data stored by google daily in 2008 was equal to 20 PB
Related article: What Is SATA 6GB/s
What are the Basic Storage Units?
The primary role of a storage unit is to provide space where we store data or the processed data. In the computing world, there are a lot of storage units. All the storage units are expressed using metrics of a kilo or mega. They are used primarily to measure capacities.
These basic storage units play a significant role for businesses, organizations, and individuals when you need the correct type of storage for your needs. There are several types of storage units: byte, kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, terabyte, petabyte.
Types of Basic Storage Units
There are several types of basic storage units as outlined below:
Byte
It is the primary storage unit in the field of computing. It consists of eight binary digits(bits), which consists of only 0 and 1. A byte can carry little information in computing. A byte is abbreviated as B while bit as b.
A bit is the basic storage unit. It normally stores one binary digit. The bits stats from 0, 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.
In modern technology, bits are represented by an electric voltage. They usually are transmitted one at a time and simultaneously. The transfer rates are measured using bits per second(bit/s).
Most of the rates SI units were invented by the International System of Units(SI).
So 1 byte has 8 bits-the byte uses 8 bits to make 256 different patterns which can store a number in the range of 0 and 255.
In the past years, bytes were commonly used for computer encoding systems, and they used to use six-bit character code.
Bytes are commonly used to present characters like letters, numbers, digits, and symbols. For example, the bits are used if a machine wants to display an image or run a particular program.
Octet
Octet consists of eight bits, and it doesn't change its composition no matter what happens. It is least used as most companies stick with bytes. It is commonly used in the telecommunications industry.
Nible
It consists of four-bit numbers. It's usually referred to as half of an octet. It is represented as a hexadecimal digit, i.e., 00-GG
Types of Bytes
Most of the storage units are made of bytes. They are usually measured in multiples of bytes. For example, a flash of 1024 megabytes counts 1024 million bytes of data.
The bytes multiples are measured using two ways: base-2 and base-10.
i) Base-2 is the binary method that is calculated by rounding off to a decimal number. For example, 210 is equal to 1 kibibyte. It is commonly used in windows operating systems, RAM capacity, cache size, billing by marketing companies like Orange.
ii) Base-10 is calculated done to the powers of 10, for example, 1 Terabyte=10004. It is commonly used in measuring the size of storage media like DVD, hard drives, flash transfer speeds, CPU clocks e.t.c
Most of the bytes have prefixes at the beginning, which helps identify the size of the byte and the data it contains. Like kilobytes-the prefix, a kilo is added to a byte to make it a kilobyte. That is how the types of bytes are formed.
Kilobyte
Kilobyte Is usually denoted as KB.
It consists of 1024 bytes. When using base 2, it can be illustrated as 10 3, and with base 10, it is expressed as 210
KB cannot measure the size of storage devices as they are minimal. They are commonly used to design graphics for small websites.
An example of a file is an email, and when sending an email, it can consist of 10KB or below unless it has many attachments, a text can be 1.8 KB, one page of the document can be 2KV.
Megabyte
Megabyte consists of 1000 kilobytes equal to 1024 kibibytes when you convert using binary method(0s ad 1s). When using base 2, it can be illustrated as 106, and with base 10, it is expressed as 220
Megabytes are primarily used in measuring the internet speed by checking king the real-time and download speed. It is also used in checking the sizes of files like music, images, videos, compressed and uncompressed videos.
Some of the computer that stores data in megabytes are CDs.
Gigabyte
Gigabyte is abbreviated as GB.
It consists of 1024 megabytes. When using base 2, it can be illustrated as 109, and with base 10, it is expressed as 240
Its mainly used in measuring Random Access Memory(RAM) of computers like HP laptop has a RAM of 4GB, measures the hard disk, e.g., my hard disk carries 500GB of data, or even a game can hold such data.
Terabyte
It's abbreviated as GB.
It consists of 1024 gigabytes. Using base 2 can be illustrated as 1012, and with base 10, it is expressed as 240.
It is mainly used for measuring storage units in large devices. Some HDD workstations are built using terabytes as a storage unit.
Petabyte
It is abbreviated as PB.
It consists of 1000s terabytes. While using base 2, it can be illustrated as 105, and with base 10, it is expressed as 250
It is sporadic for this to be used on intermediate storage. It is used on large servers in companies like Google, Facebook, Amazon e.t.c
Exa Byte
It is abbreviated as EB.
It consists of 1000 EB. When using base 2, it can be illustrated as 1018, and with base 10, it is expressed as 260
It's primarily used in calculations. Even the servers cannot use Exabyte as a storage unit as it's so big and exceeds the standard storage units.
We can use it to measure data of different servers or networks, like finding out the data transferred over the internet for six months.
Zetta byte
Zetta byte is abbreviated as ZB.
It consists of 1000 exabytes. While using base 2, it can be illustrated as 1021, and with base 10, it is expressed as 270
They are used in measuring large amounts of data, i.e., they can calculate the actual data of the world.
Yotta Byte
It is the largest storage unit, and it consists of 1000 zettabytes. When using base 2, it can be illustrated as 1024, and with base 10, it is expressed as 280
There is no actual application of yottabyte as the word data is around a few zettabytes. It is even hard for human beings to come up with calculations of a yottabyte. The visualization becomes harder.
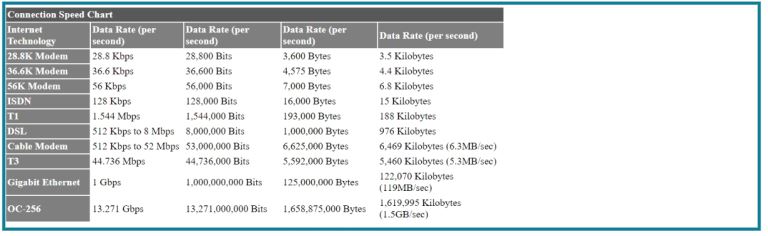
Connection Speed Chart
| Internet Technology | Data Rate (per second) | Data Rate (per second) | Data Rate (per second) | Data Rate (per second) |
| 28.8K Modem | 28.8 Kbps | 28,800 Bits | 3,600 Bytes | 3.5 Kilobytes |
| 36.6K Modem | 36.6 Kbps | 36,600 Bits | 4,575 Bytes | 4.4 Kilobyte |
| ISDN | 128 Kbps | 128,000 Bits | 16,000 Bytes | 15 Kilobytes |
Why is 1gb equal to 1024 MB?
Technically, there are 1024MB (megabytes) in one GB (gigabyte). And This is because computers are based on binary systems- Which indicates that memory and hard drives are measured in powers of 2.
If you dive deeper, there are 1024 gigabytes in a terabyte (TB) and 1024 terabytes in one petabyte (PB). All these are storage capacities. They can refer to hard drives or memory RAM.
What is a megabyte?
The storage of a computer is measured in gigabytes and terabytes, plus other units. Your smartphone also has several gigabytes to store music, apps, messages, photos, videos, etc.
Don't be mixed up on storage and memory (RAM); RAM only stores some data and files temporarily as they are being used. That's why it has a smaller capacity.
The hard drive in your laptop probably has hundreds of gigabytes. Network-attached storage (NAS) and external hard drives have a similar capacity or even thousands of gigabytes, called terabytes.
Here is how it illustrates:
- 1TB=1024GB
- 1GB=1024MB
- 1MB=1024KB
- 1Kb=1024 Bytes
- 1Byte=8 bits
- 1bit=0 or 1
Although, this is not included in the SI units, which perform on the idea that kilo means 1000.
There are two ways of qualifying storage; the first uses the power of 2, and the other uses the power of ten, making 1KB equal to 1000bytes. And this is why you'll see kilobytes being referred to as kibibytes and megabytes as mebibytes are to differentiate them.
Computers and laptops perform using the power of two and not ten as they are binary machines. The binary interpretation of metric prefixes is used by Microsoft Windows operating systems.
Because of the prevalent binary addressing of memory, you can use the metric prefixes for random access memory capacity like main memory and CPU cache size.
What is meant by digital storage?
In today's world, we are surrounded by computers. It could be for business purposes or personal use, and your valuable data, you need a place to store it.
Digital storage makes use of storage memory to keep data. To better hold your information, you need to acquire knowledge of different types of storage devices. Here are basic kinds of storage devices.
- Magnetic storage
The most common types of digital storage which use this storage technology are; hard disks, floppy disks, and tape recorder cassettes.
This kind of storage requires a channel such as an organic metal for encoding data. Hard disks have round platters inside, made of metal oxide materials. They roll at high speed around a spindle.
The mechanical bit- referred to as the armature. The head is responsible for writing and reading patterns of the magnetic polarities—the prints, stored in parts just by magnetizing the platters. The hard disk is the most preferred type of digital storage. Laptops and tablets mostly use magnetic storage.
- Optical storage
In this type of storage technology, you'll require two things—the optical drives and the visual media found in the form of circular discs.
They feature a laser beam used for lightning, which reflects on the photodiodes generating a voltages pattern. The information is read and written by the optical review or the laser.
The following is how you can use the technology- primarily;
Compact disc (CD)- For storing music files and programs. Although its storage capacity is considered pretty low at 700MB.
Digital versatile disc (DVD)- You can use it for storage of standard-definition movies. It uses red laser rays.
Blue-ray disc (BD)- it has a larger capacity than the above two. Use it for the storage of high-definition movies.
- Solid-state storage
This kind utilizes non-volatile memory. It's got the ability to retain information even when power is off. It doesn't have moving parts as compared to optical and magnetic storage.
Solid-state is more efficient compared to conventional hard drives. They don't encode data from platters; instead, they use flash memories which allows the data to be written, deleted, and rewritten when necessary.
This technology is faster, quieter, and lighter. It is also very efficient and more expensive and consumes less power. Below are some common forms of solid-state storage;
Flash memory cards-digital cameras, navigation devices, and smartphones benefit from this kind of digital storage. The standard formats are MemoryStick, MicroSD, compact flash, and secure digital.
USB flash drive- commonly referred to as a USB. It is stick-like portable storage that comes in small sizes. You need to plug it into the USB port to use it. Super speed is among its top benefits.
Flash hard drives- these are portable devices. They are used mainly by laptops and tablets to store information. They possess the same shape as mechanical hard drives but come in smaller sizes.
How digital storage makes your business more productive.
They reduce the storage space of the documents. With the need to keep your documents safe, paper-based storage has become an expensive expenditure. With digital storage, you can access the documents easily or retrieved when needed.
It also saves up on space as you won't need to have cabinets lying around your office-This will allow you to make other areas more productive for other business purposes.
Digital storage allows you to share data more efficiently. In any business, sharing documents and files with your staff, clients, and colleagues is a vital need for your company.
With the help of digital storage, there's no need for photocopying documents lest you need more. There will be no extra cost in printing.
They provide security and safety to your documents as you are allowed to set restrictions. You can control who can access them with the aid of a password and choose whom you'd like to share the files with it.
Digital storage helps in data recovery. If you lose your data due to theft, fire, vandalism, etc., you can quickly recover it if you had stored it online with a backup.
You can access your data anywhere as long as you have internet-This allows you to see changes and updates on time. They also allow you to update your data quickly.
Conclusion
The storage technology has advanced in just a few decades, and you can imagine what the future holds. You can now store large amounts of data like music videos, images and audio in our smartphones or computers- a thing that was impossible a few decades ago.
Read also: What Is a Computer Hard Drive Used For?