How do you fix a computer that won't turn on?
If your computer won't turn, follow the five major steps highlight in this article. You will know the source of the issues and possibly resolve them.
It is annoying when your computer can’t turn on, and it’s even more hectic to know how to fix it. The first and important step is to troubleshoot. It will help you understand the problem, fix it, and go back to using your computer.
Modern computers are complex. It’s not obvious to know diagnose and fix an issue as fast as you might want. There is a variety of hardware configurations that make it hard to diagnose each problem on your computer.
We will cover a step-by-step process that will enable you to fix your computer if it’s not turning on. This process can be used to fix a computer that hasn’t turned on before or the one that has operated normally before.
Before we jump into the first step, let us have a look at how to diagnose.
Diagnosis of a computer that won’t turn on
A ‘computer not turning on’ can mean a lot. For this article, we assume the following scenarios:
- a) That your system is not reacting when the power button is pressed
- b) That it’s turning on for a few seconds, then shuts down.
Throughout this process, we will be talking in detail about various computer hardware. However, not every issue might apply to you. So, feel free to start with the step that best suits you.
Let’s jump into the steps to diagnose why your computer won’t start.
Step one: Check Cables
If the LEDs on your computer’s internal components are lighting up, then you don’t need to check your cables.
If the components are not lighting up, first check the cable from your wall.
- a) Check if the wall outlet cable is working by inserting another device like a charging phone, and see if it’s working properly.
- b) Ensure that the power strip or surge protector is properly plugged into the outlet and that the switch is on. You can plug it into other devices to check if it’s working correctly.
- c) Check that your computer power supply is on/off switch is on.
- d) The computer power cable can be loose with time. Ensure that the cable is properly plugging into the power system and the outlet power source.
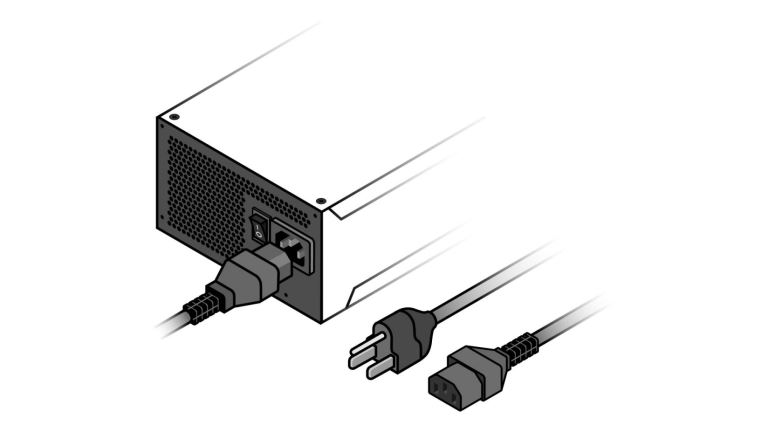
Now that you have checked the connection from your wall to your computer, it’s time to check the computer cable that plugs into PSU. This cable is called C13.
- a) In many instances, monitors and Desktop PSU use the same C13 cables. If that the case for you, swap the monitor cable with the computer cable and see if the monitor will turn on. If it doesn’t work, test your computer with the cable that was powering your monitor.
- b) Ensure you have a spare C13 cable. Note that some computers are power-hungry. So, when you are buying a spare C13 cable, ensure you get a similar gauge to the one you have been using. Some have higher gauge cables. Keep that in mind.
After confirming that the C13 and outlet cables are functioning properly, the computer won’t turn on? It’s time to check the internal cables inside your case.
Step two: Internal Cabling
Here, you check the wiring inside your case to ensure no loose or malfunctioning cables. If your system is prebuilt, note that you will violate your warranty if you open your computer. Before you proceed, contact your manufacturer for advice.
For your safety, unplug the cable that connects your computer and outlet before you start working on anything. Make sure you disconnect the externals like mice, external hard discs, keyboards, and cables that connect your computer and monitor.
Display connections cables or USB devices can cause power malfunctions. If your computer boots without any plugged in, plug in each one of them and check if you find any peripheral with an issue. Or, boot without it or test with a spare one.
If the issue is not resolved, remove the connection from the wall power source, and open your computer to access internal components. This process is different depending on each case. So, use the right instructions according to your system. The manufacture must have given out guidelines to access your internal computer components.
Once it’s open, check if you see any loose cables from the power supply to the component in your computer. Reseat all that are loose. If your system is modular PSU, ensure that the cables are well seated on the PSU side. If all cables are okay, check if the computer turns on.
Still not turning on? Unplug all power cables connected to the components, such as CPU cables connected to the motherboard, 24-pin cables to any PCIe gadgets like SATA and GPU, and Molex power connectors.
Start by reconnecting all the cables to each hardware and test to see where the problem is in each hardware.
Check if there is anything that is causing electrical shock. An electric shock can be caused by a motherboard screwed to the case without appropriate standoffs. Also, Molex connectors with errant pins can cause electric shocks. This is unlikely for many computers, but it’s worth checking.
If all that doesn’t work, you could be dealing with a faulty PSU. Use a spare power supply and plug in the CPU and 24 Pin motherboard cable from your new PSU and check if it provides power to the motherboard. If this works, you have a faulty PSU, and you need to contact your manufacturer for directions.
Step three: Hardware, POST codes, and Motherboard tests.
If the LED lights on the internal hardware are working and still not powering properly or shuts down after seconds, it’s time to try the following steps.
POST and Beep codes
POST means Power On Self Test. While it’s hard to pinpoint reasons why your computer is not booting, it is possible to use built-in tests to realize where the issue is. Beep and POST codes are audio and visual cues that manufacturers use to communicate hardware tests.
POST codes have two numbers that indicate where the problem might be in the system while booting. This can help you identify where the source of the issue. If your system has no built-in display, you can get a POST test card installed into a PCIe slot. This will display codes for you.
Beep codes are the ‘audio version of POST codes. If your computer is turning on, you might hear some beeps. For instance, if it beeps thrice, it can mean the video card is not available. You will need to reseat your GPU.
Every manufacturer uses a different coding system. Check the motherboard documentation for your manufacturer to know exactly the meaning of audios and visuals from your system.
Motherboard BIOS update
If you have followed the steps stated above and no POST codes, you need to ensure that the motherboard’s BIOS is updated.
The process varies depending on your manufacturers. You can get their documentation or search online for a specific computer brand manufacturer.
Step four: Power Button
The computer won’t turn on? Having gone through all those steps and still not working, the problem can be the power button or the cables connecting it to the motherboard.
You can use a screwdriver to jump-start your computer- if the motherboard has no onboard power button.
Follow these steps:
- a) Trace the power switch headers- two of them, on the motherboard. If the power button is already is connected to the headers, remove the cables. If you can’t locate the power button switch, consult your manual. They have different labeling.
- b) Ensure that the PSU is on, and the CPU and 24-pin motherboard cables are connected, and the power cable.
- c) If everything is connected properly, the system will turn on when you use a screwdriver to connect the two power switch header pins.
Step Five: Components Test
If your computer is not turning on, you need to start testing all hardware pieces individually. Here you test the connections to the motherboard and make sure all the hardware pieces are communicating well with the rest of the system.
Remove the GPU, any storage, unplug everything from I/O, and all but one stick of RAM.
If your computer is turning on with minimalist set up, add a hardware piece and power down. Continue with this process until when the system fails to boot, that is where the problem is.
Finally….
If you have tried all the steps above, and still your computer is not turning on, you might be dealing with a faulty CPU, PSU, or motherboard.