If you've ever worked with codes, you're probably familiar with the Command Prompt. The Command Prompt is a program that is installed on all Windows computers and allows you to manage the computer with text commands. However, unlike other apps, the Command Prompt is not always easy to locate.
There are several ways to open Command Prompt on Windows 10. The Power User Menu, which you can access by right-clicking the Windows icon in the bottom-left corner of your screen or by the keyboard shortcut Windows Key + X, is the quickest way to open a Command Prompt window. It will appear twice in the menu: Command Prompt and Command Prompt (Admin).
This article will show you the best ways to open Command Prompt on Windows 10 and all basic Command in Command prompts— and how you can use them. Read on to know when and how you can use Command Prompt.
How to Open the Command Prompt in Windows 10
The Command Prompt was launched in the late 80s. Due to its popularity, Microsoft has made it easy to access it in different ways.
However, in the latest Windows 10 version, Microsoft seems to replace Command Prompt with Windows PowerShell. This means you can run similar commands on PowerShell as you will do on the Command Prompt App.
Every Windows power user understands that opening a Command Prompt window is frequently the quickest way to get things done— just like keyboard shortcuts. For some tasks, it is the only way. Here's a list of the best ways to get to the command line on Windows 10:
Use Run App to Open Command Prompt on Windows 10
The Run app can be used to open programs, documents, and folders on your Windows 10 computer. Similarly, you can use the same app to open the Command Prompt.
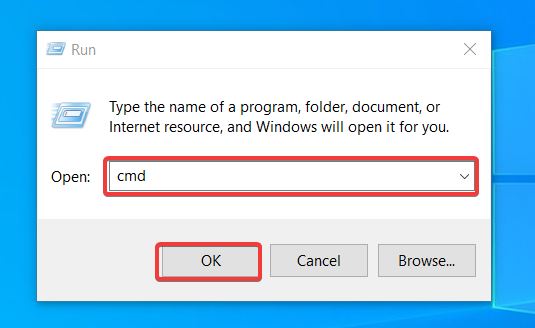
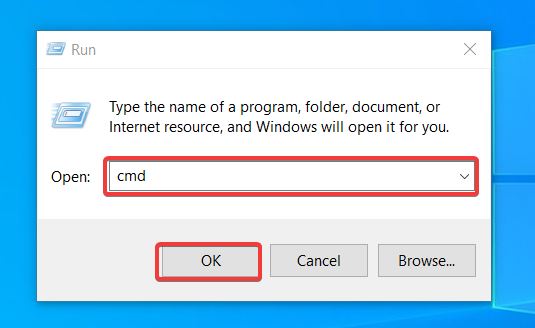
There are two main ways to open the Run app: by pressing the Windows button + R or searching the Run app on the search box.
Once the app is open, you will see a text box. Type cmd to open the app. You can then click OK, or press Enter on your keyboard.
Use the Windows PowerShell to open the Command Prompt on Windows 10
The command I will use in this method is the same one you can use on the command prompt to open the command prompt.
To open the Windows 10 Powershell, open the Run app by pressing the Windows button + R. Type powershell in the text box on the Run dialog window. Press Enter on the PC keyboard or click OK.
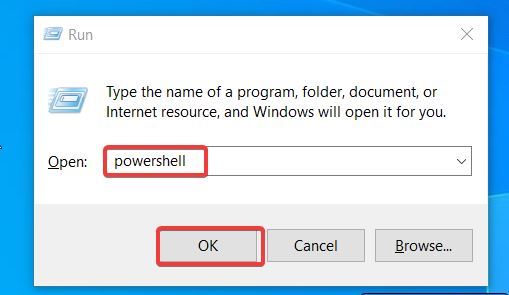
This method will open regular Windows PowerShell if you want to open the elevated PowerShell Window, press Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
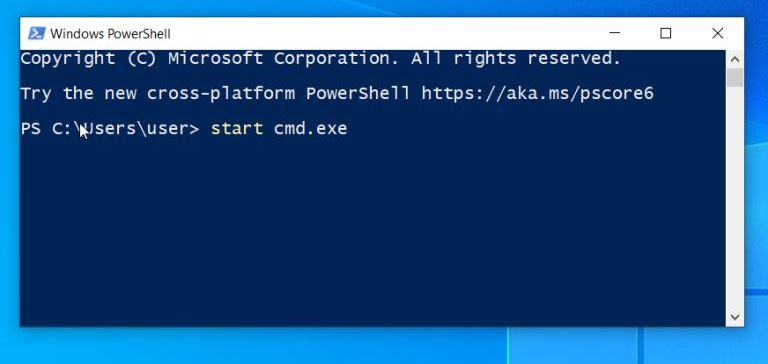
Once the PowerShell is open, type this command: start cmd.exe and press Enter.
Use Search Box to open the Command Prompt on Windows 10
The Windows Search is a tool to search any app inside your computer. You can do the same to open the Command Prompt.
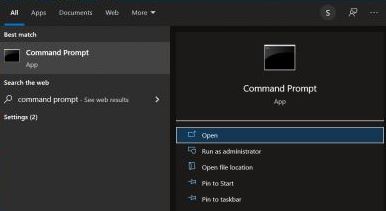
Type Command Prompt on the Search box found on the bottom-left side of your computer screen. The search results will show Command Prompt. Click on Open on the right side of the search results, as shown in the screenshot below.
Use Task Manager to Open Command Prompt on Windows 10
There are two methods to open Command Prompt from the Task Manger— the quick one and the quicker one.
Quick one: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc.

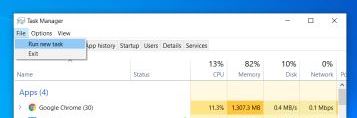
Once open, click on the File tab. From the drop-down menu, click Run New Task.
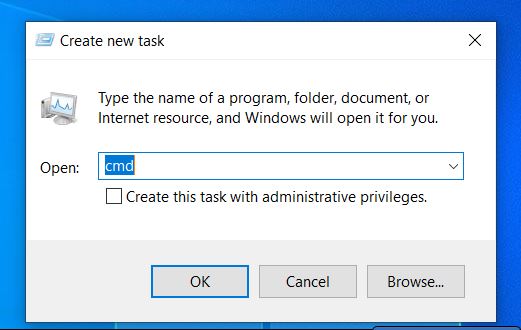
A new window will appear— Create New Task. On the text box against Open, insert this character: cmd. Click OK or hit Enter to open the Command Prompt.
The Quicker one: Here, you press and hold on the Ctrl button while clicking on the New Task Task tab on the Task Manager File drop-down menu. The Command Prompt will appear immediately without typing anything as I did on the Quick method above.
Use .exe Command Prompt File to Open Command Prompt.
This method sounds like a tongue twister, but let me simplify it for you.
Each PC program has an executable file. Once you double click on those files, the respective program will launch.
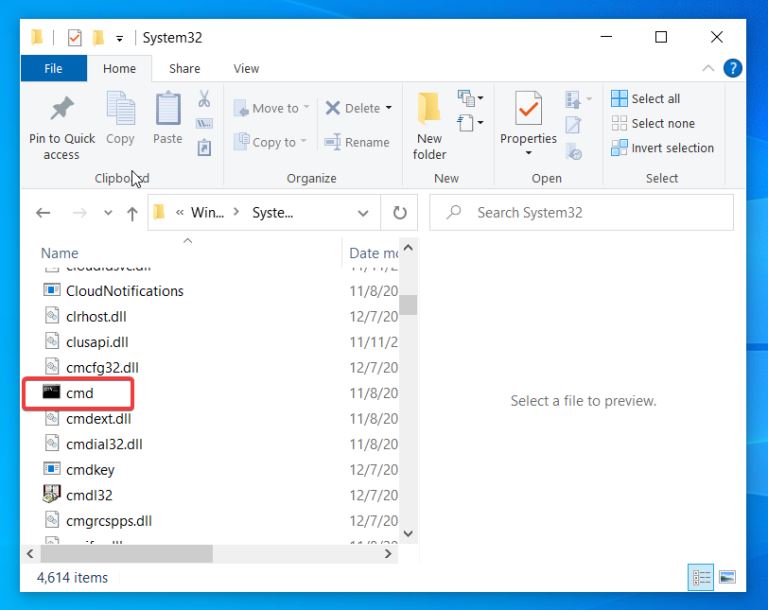
To open the Command Prompt .exe file, go and open File Explorer (Check it on your local Disk {C.}). Open the System Folder then Windows then System32.
On System32, scroll down looking for Command Prompt .exe file. To open the cmd, double-click on the file— Command Prompt launches.
Use Start Menu to open Command Prompt on Windows 10
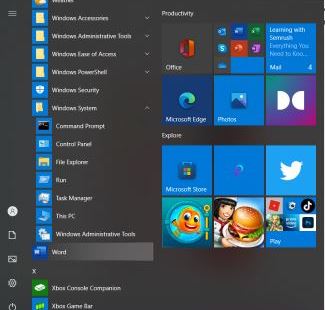
On the bottom left corner, click on the Windows Icon the scroll down looking for Windows System. Click on the down arrow to view the drop-down items on the folder.
There are several items listed under the Windows system. Click on the Command Prompt.
Use WinX Menu to Open Command Prompt on Windows 10
WinX menu is also referred to as Power User Menu. There are two ways to launch the Power User menu; the first one is by pressing the Windows button + X and the second one is by right-clicking on the Windows icon on the bottom left corner of your computer screen.
From the list, look for the Command Prompt or Command Prompt(Admin) as shown in the picture below.
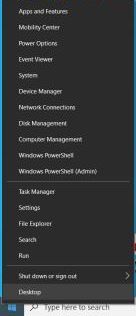
NOTE: This method can only work with older versions of Windows 10. Microsoft replaced Command Prompt with Windows PowerShell on the list of the latest Windows 10 version.
Use Cortana to Open the Command Prompt on Windows 10
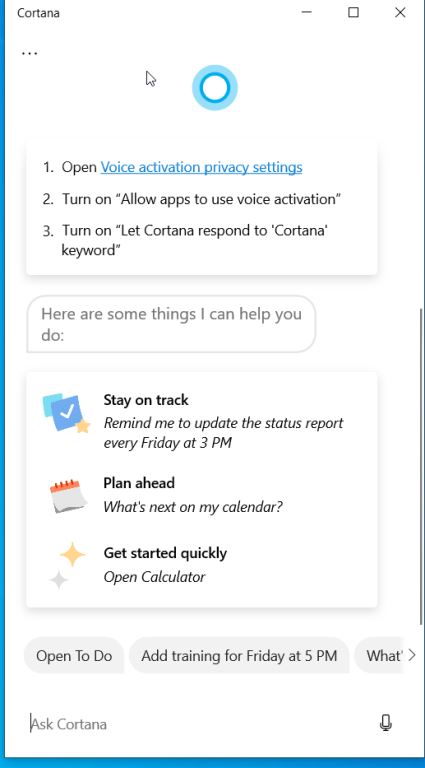
Cortana is the Windows 10 digital assistant— you can ask it to open Windows 10 Command Prompt. Click on the Cortana from the taskbar to open it.
To launch the Command Prompt, click on the Cortana app on the taskbar. Click on the microphone at the bottom-right side of the Cortana app. Say 'open Command Prompt' and the app will open the command prompt window immediately.
If your microphone on the Cortana app is not working or you don't feel like speaking, you can go ahead and type 'open command prompt' on the Cortana search bar.
Use Command Prompt to open Command Prompt on Windows 10
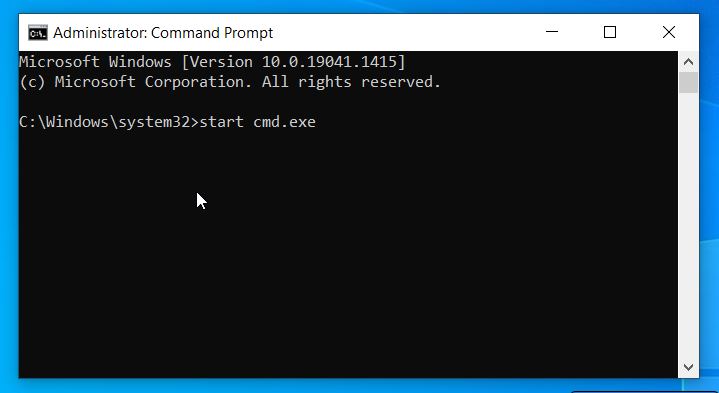
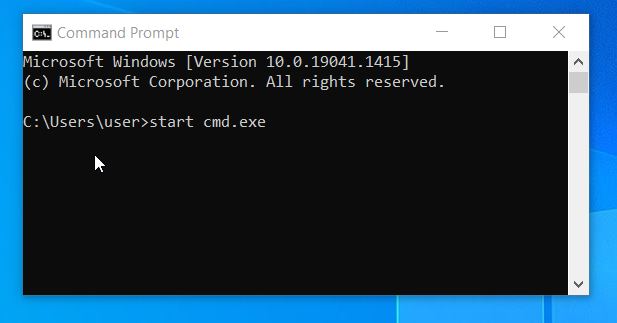
At times, you might want to have two sessions of command prompt on your computer. To achieve that, you can use the command to open the second one— while on the first session.
While on the first Command Prompt, run this command: start cmd.exe and press Enter. This will open a new Command Prompt window instantly.
Use File Explorer to open Command Prompt on Windows 10
This is quite a simple method. All you need is to type System32 on the address bar at the top of the Window and hit Enter. Use the folder 'This PC' to type in the character above.
Right-click on the file cmd, and select Run as an Administrator.
What are the basic commands in Command Prompt?
There are about 300 commands in Command Prompt. Below is a table of the basic Commands on windows 10 Command Prompts:
| CMD command | Function | Example in Use |
| bitsadmin | Monitors uploads and downloads |  |
| xwizard | Registers data in form of XML files |  |
| wmic | Launches Windows Management Instrumentation. You can change local and remote computer settings here | 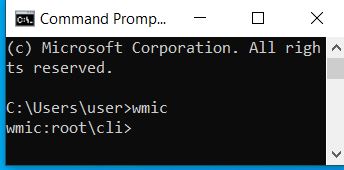 |
| winmgmt | It is a command to manage WMI repositories, eg. You can initiate backups with this command | 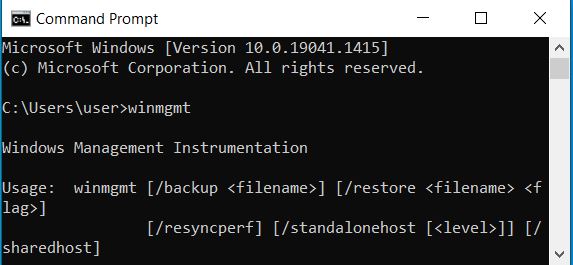 |
| ver | It displays the current version number of MS-DOS or Windows | 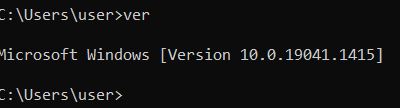 |
| tzutil | Shows the current time zone or changes it | 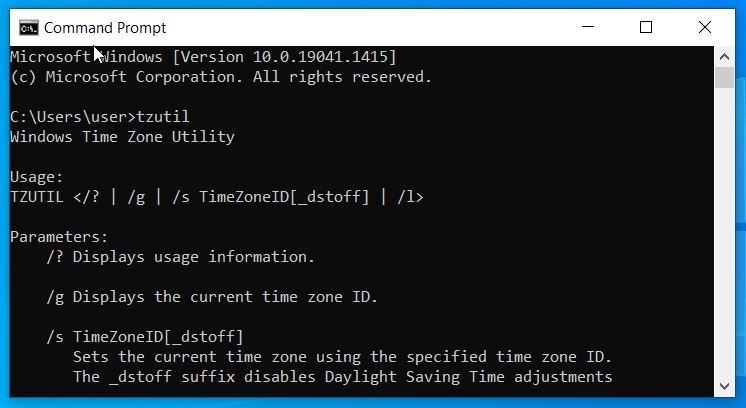
|
| title | This changes the title of the command prompt. Some special characters like slash are not allowed as they might be interpreted as parameter instructions. Spaces are allowed, though. | 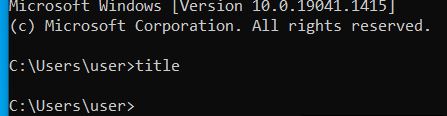
|
| tree | It displays the structure of a path or drive. With /F, all folder files are listed out. With /A, ensures only ASCII characters are used in the graphical representation. | 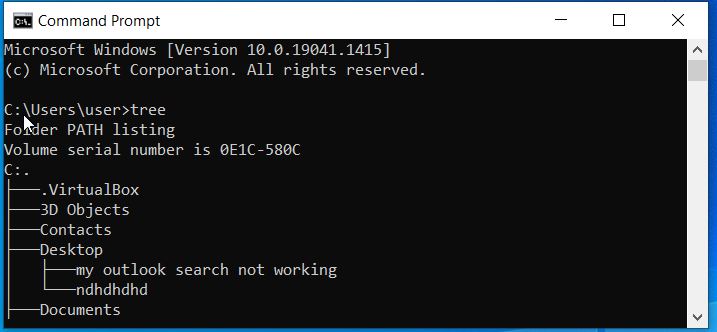
|
| time | Shows the current time and allows you to change it. If you enter /T, the command prompt displays time without changing it | 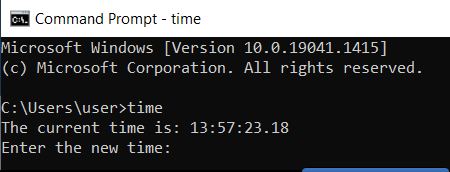
|
| timeout | It is used in batch scripts and files to stop a specified process. eg /nobreak parameter ignores keyboard input. | 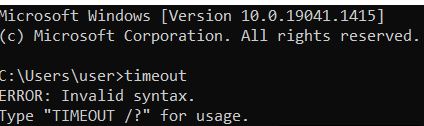
|
| tasklist | All running processes are listed here. You have to specify the process ID required for the taskkill command. | 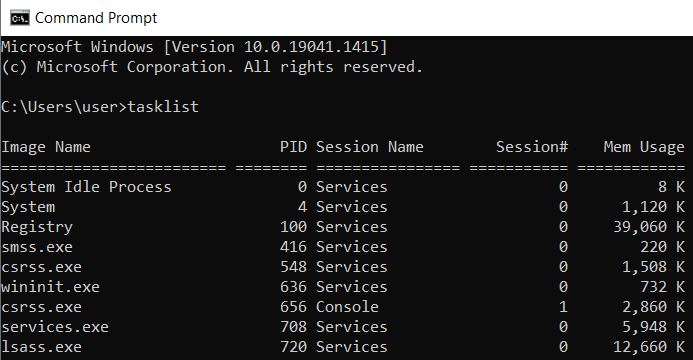
|
| cd | Shows the current directory and lets you switch to others. it has the same command as chdir | 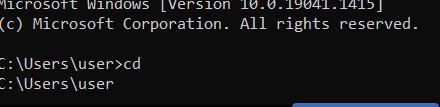
|
| choice | Creates a selection of lists— eg. the selection of Yes (Y) and No (N) that is created with /C YN. /M adds an explanatory text to the user | 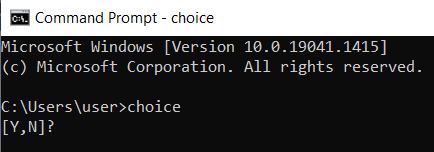
|
| chcp | Changes the current code page (character set table) or displays the current code page's page count. | 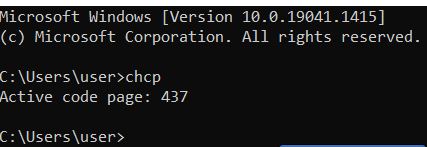
|
| chdir | Displays the current directory and allows you to switch between them. You can also switch drives using the parameter /D plus drive and path specification. To move to a higher directory, use chdir— which has the same function as the cd command | 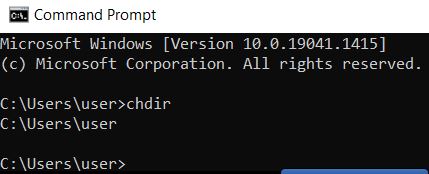
|
| clip | The result of a command is copied to the clipboard. You can copy the directory structure (dir clip) or the content of a file (clip filename) to the clipboard, for example. | 
|
| cls | Clears the screen's content. | 
|
| color | Changes the command prompt's background (first value) and text color (second value). The color ranges from 0 (black) to F. (white). | 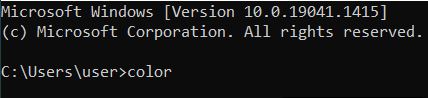
|
| cmd | Launches cmd.exe. | 
|
| command | Launches cmd.com. | 
|
| doskey | Creates macros, edits command edits, and recalls commands | 
|
| date | Debug, a program that can test and modify programs within the command prompt, is launched. | 
|
| dir | Debugs, a program that can test and modify programs within the command prompt, is launched. | 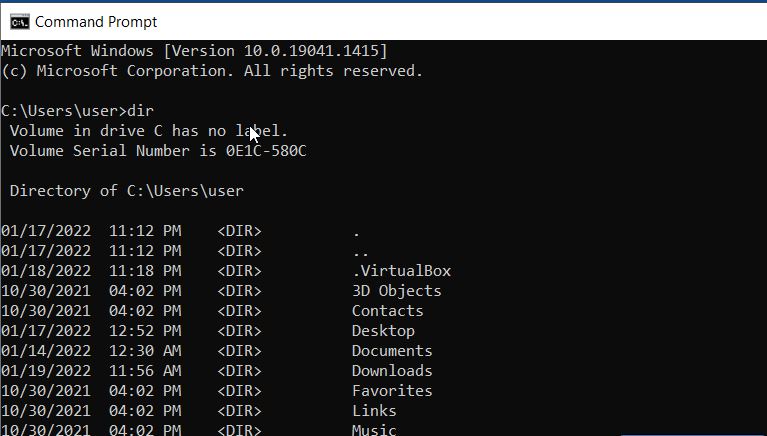
|
| dosshell | The DOS shell, a visual file management tool, is launched. Windows Explorer replaces the DOS shell in Windows. | 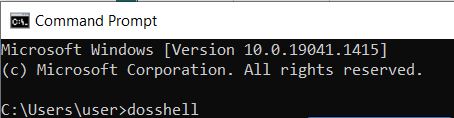
|
| fastopen | Writes a program's position into a specified list in working memory, which should speed up program startup. | 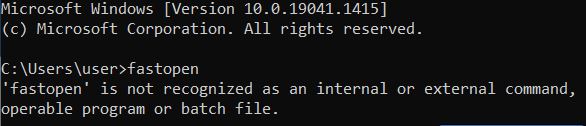
|
| echo | Displays a message and is most commonly found in scripts and batch files. | 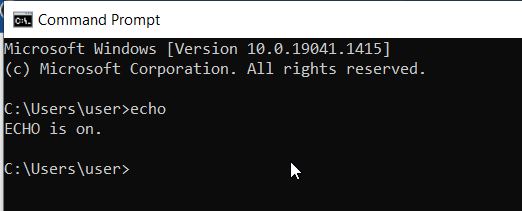
|
| edit | Starts the MS-DOS editor, which can be used to create text files. | 
|
| exit | Ends cmd.com and cmd.exe | You can't see it. It's gone |
| edlin | Within the command prompt, it creates and edits text files. | 
|
| fasthelp | Shows important information about command prompts | 
|
| debug | Debug, a program that can test and modify programs within the command prompt, is launched. | 
|
| fastopen | Writes the position of a program into a specified list in working memory, which should speed up program startup. | 
|
| findstr | Character sequences can be found in one or more files. When compared to the find command, it provides more options: you can search for files that contain specific terms, or you can search for an exact word order with /C. | 
|
| find | Searches a file or multiple files for a specific character sequence. Use the /C parameter if you only want to know how frequently the word or phrase appears. The command ignores upper- and lower-case characters in the search when the extension /I is used. | 
|
| keyb | Changes the keyboard's country settings for DOS programs (only included in Windows for compatibility). In newer versions of Windows, kb16 has taken its place. | 
|
| forcedos | Starts a program in the MS-DOS partial system if it is not directly recognized as a DOS program by Windows XP. | 
|
| graftbl | In graphics mode, this option enables the use of extended characters from a specific code page. | 
|
| kb16 | Changes the keyboard's country settings for DOS programs (only included in Windows for compatibility). (Replaces the previous command keyb) | 
|
| graphics | Starts a graphics-printing program. | 
|
| help | Displays help text for a specific command (the /? command can also be used). | 
|
| lpq | For computers that use a "line Printer Daemon," this command displays the status of a printer queue (LPD). (To use the command in Windows 10, 8, 7, or Vista, first enable the LPD print service and the LPR port monitor.) | 
|
| logoff | This command logs the user out of Windows. You can also terminate server sessions. | Do it if you want to log off out of the Windows |
| mkdir | On the specified path, it creates a new directory. If a directory does not already exist on the path, mkdir creates it (you can also use the md command). | 
|
| md | On the specified path, it creates a new directory. If directories do not already exist on the path, md creates them (you can also use the mkdir command). | 
|
| lpr | Sends a file to a computer equipped with a line printer daemon (LPD). To use the command in Windows 10, 8, 7, or Vista, first enable the LPD print service and the LPR port monitor. | 
|
| msg | Sends a file to a computer that has a line printer daemon running (LPD). To use the command in Windows 10, 8, 7, or Vista, you must first enable the LPD print service and LPR port monitor. | 
|
| more | The page outputs the content of a file (for example, a text file). The command can also be used to divide the output of another command into pages. | 
|
| pushd | This function saves a specific path to a script or batch file. With popd, you can navigate to this directory. | 
|
| nlsfunc | Provides country-specific language support information. | 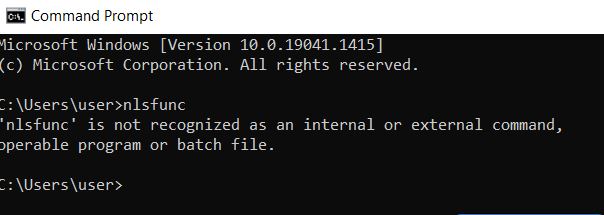
|
| prompt | This command modifies the appearance of the command prompt. | 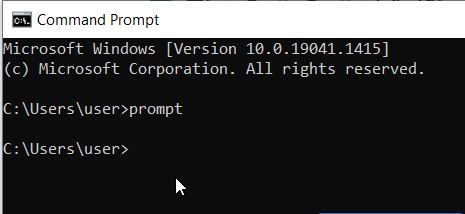
|
| print | This function prints a text file. It is necessary to specify the printing device. | 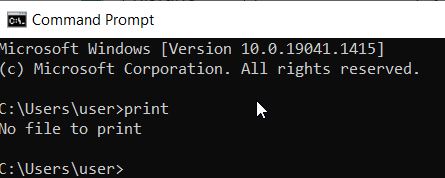
|
| ntbackup | Backup services can be started directly from the command line or as part of batch or script files. | 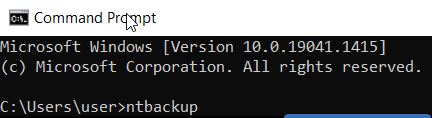
|
| popd | Backup services can be launched directly from the command line or as part of batch or script files. | 
|
| pause | Stops the execution of batch files and scripts. The user is then prompted to continue by pressing a key in a message. | 
|
| path | The path for searching executable files is created and displayed. | 
|
| shutdown | Shuts down the computer (/s), triggers a restart (/r), or logs the user out (/l). If you enter the parameter /I as the first option in the command, a graphical user interface is displayed. | 
|
| rd | This command deletes a directory. This must not contain any files, even if they are hidden. The /S parameter allows you to delete an entire directory tree (you can also use the rmdir command). | 
|
| rmdir | This command deletes a directory. This must not contain any files, even if they are hidden. The /S parameter allows you to delete an entire directory tree (you can also use the rd command). | 
|
| schtasks | Sets the execution of specified programs and commands for a given time period. All scheduled tasks can be created, deleted, changed, and displayed. | 
|
| runas | Allows one user to execute commands with the rights of another. For example, if you know the password, you can run a command as an administrator from a normal user account. | 
|
| shift | Variables are moved within batch files and scripts. | 
|
| start | Opens a new command prompt window where you can execute a specific program or command. | 
|
| change | The change command modifies terminal server settings such as installation modes, COM port mappings, and logons. | 
|
| chkntfs | The chkntfs command is used to configure or display the disk drive's checking during the Windows boot process. | 
|
| cscript | The cscript command is used to run scripts through Microsoft Script Host. The cscript command is available in all Windows versions. The cscript command is most commonly used to manage printers from the command line by executing scripts such as prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmngr.vbs, and others. | 
|
| diantz | The diantz command is used to compress one or more files losslessly. Cabinet Maker is another name for the diantz command. | 
|
| netsh | The netsh command launches Network Shell, a command-line utility for managing the network configuration of a local or remote computer. | 
|
| nltest | The nltest command is used to test secure channels between domain computers and domain controllers that trust other domains. | 
|
| reg | The reg command is used from the command line to manage the Windows Registry. The reg command can be used to perform common registry functions such as adding registry keys, exporting the registry, and so on. | 
|
| regini | The regini command is used from the command line to set or change registry permissions and registry values. | 
|
| regsvr32 | The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file in the Windows Registry as a command component. | 
|
| secedit | By comparing the current security configuration to a template, the secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security. | 
|
| sfc | The sfc command is used to check and replace critical Windows system files. Depending on the operating system, the sfc command is also known as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker. | 
|
| sxstrace | The sxstrace command launches the WinSxs Tracing Utility, which is a programming diagnostic tool. | 
|
| vssadmin | The vssadmin command launches the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool, which displays all installed shadow copy writers and providers as well as current volume shadow copy backups. | 
|
Conclusion
Microsoft is replacing the Command prompt with Windows PowerShell. There is no apparent reason, but you can still use the same commands you used.
Windows PowerShell is a more recent program that functions similarly to Command Prompt. Some versions of Windows 10 replace Command Prompt in the menus where you'd generally find it.
PowerShell has nothing wrong; it can do pretty much everything Command Prompt can, but if you're used to it, it's simple to switch back. You can use the command to perform many tasks on Windows 10, including opening task manager.